SuperCollider: Light Dependent Resistor
This example shows how a single sensor can be streamed via serial data from the Arduino to SuperCollider.
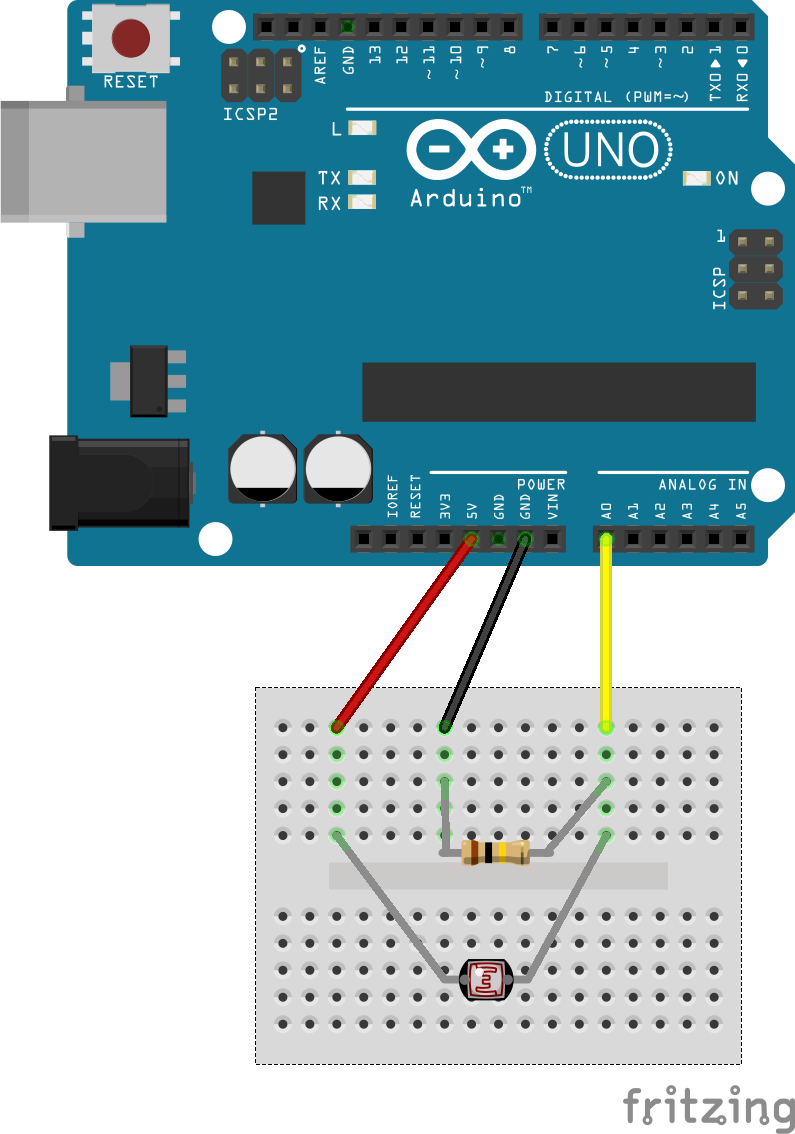
Breadboard Circuit
The breadboard circuit is the same as in the first Arduino sensor example:
Arduino Code
For the SC example, serial data is sent in a simple way. The additional scaling is optional, but makes it easier to process the data in SuperCollider.
void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { int sensorValue = analogRead(A0); // scale to 0..1 float voltage = sensorValue/1024.0 ; Serial.println(voltage); }
SC Code
On Linux, the Arduino's serial interface can be found in the terminal:
$ ls -l /dev/ttyACM*
On the SC receiver end, a serial port object is initialized with the matching serial interface:
( p = SerialPort( "/dev/ttyACM0", baudrate: 9600, crtscts: true); )
A control rate bus is used to visualize the received data and make it accessible to other nodes:
~sensorBUS = Bus.control(s,1); ~sensorBUS.scope;
The actual receiving and decoding of the data happens inside a routine with an infinite loop. It appends incoming characters, until a return character (13) is received. In this case, the assembled string is converted to a Float and written to the sensor bus:
( r= Routine({ var byte, str, res; inf.do{|i| if(p.read==10, { str = ""; while({byte = p.read; byte !=13 }, { str= str++byte.asAscii; }); res= str.asFloat; // ("read value:"+res).postln; ~sensorBUS.set(res); }); }; }).play; )
External Resources
The SuperCollider Tutorial by Eli Fieldsteel shows a similar solution for getting Arduino sensors into SuperCollider via USB.
Exercise
Exercise
Create a synth node with a parameter mapped to the sensor bus.
