Python for Sequencing
Python offers many useful tools for preparing data and controlling synthesis processes. Although it can also be used for digital signal processing and sound synthesis, its versatility makes it a great tool for auxuliary tasks. Most notably, it can be used for flexible processing and routing of OSC messages, especially in the field of data sonification. In this example, Python is used as a sequencer - the script reads data from a csv file and plays it back. The data is sent to PD via OSC for sonification.
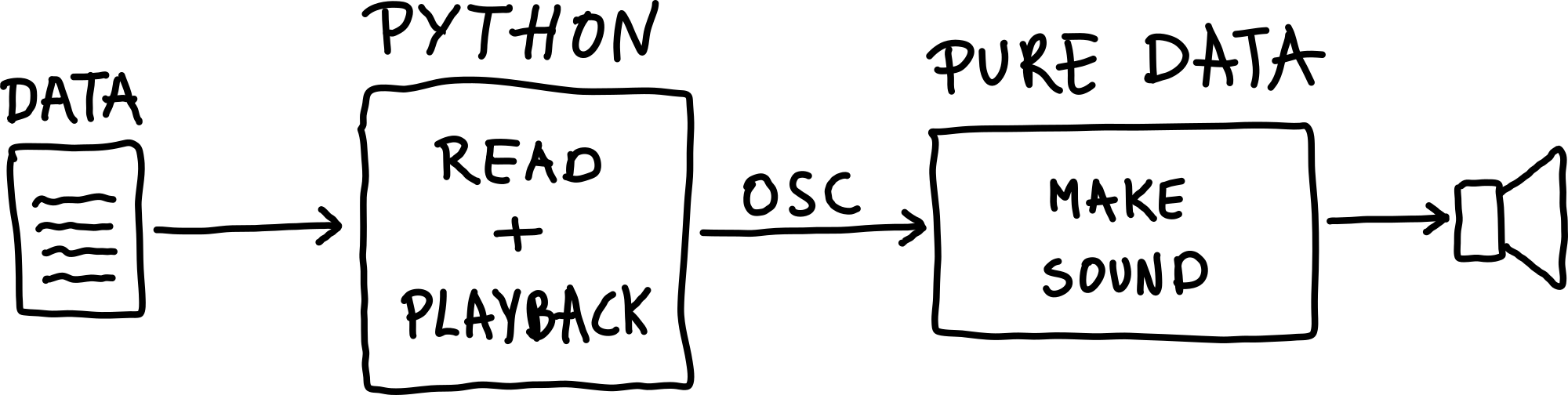
Figure: Using Python for sequencing with Pure Data.
Example: First Sonification
This repository contains everything - Python scripts and Pd patches - but the data: https://github.com/ringbuffer-org/first_sonification. Clone the repository to get started.
Data
This example needs tab-separated text files as input, accepting multiple time-series in one file. It needs to be in formatted as follows:
Each column represents a single time series.
Each row corresponds to a sample inside a time series.
All time series in the data have the same number of samples. An example for a file with two time-series, each with 10 data points (samples):
0.12, 1.03 0.15, 0.98 0.22, 0.91 0.35, 0.87 0.48, 0.82 0.62, 0.79 0.71, 0.74 0.83, 0.69 0.94, 0.63 1.02, 0.58
Python
The Python script is minimalistic, consisting of 3 code blocks:
1: Argument Processing
2: Read Data
3: Playback Loop
It relies on numpy and python-osc - the installation is covered in the repository.
The script can be executed like this:
$ python3 sequencer.py PATH_TO_FILE --col 1 --interval 100
The arguments explained:
--col: Determines which column will be used.--interval: Determines the sampling rate of the playback (how long does the script wait to send the next sample).--port: This optional argument can change the port the script is sending the OSC data to.
Pure Data
This example builds on the introduction patches on Using OSC in Pure Data.
It receives incoming OSC data and uses the message with the path /val.
The incoming values are scaled and then turned into a tone with changing pitch, using the osc~ object, which is sent to the audio output with dac~:
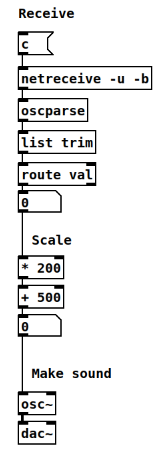
Figure: Using Python for sequencing with Pure Data.
It might be necessary to review+ the following sections:
